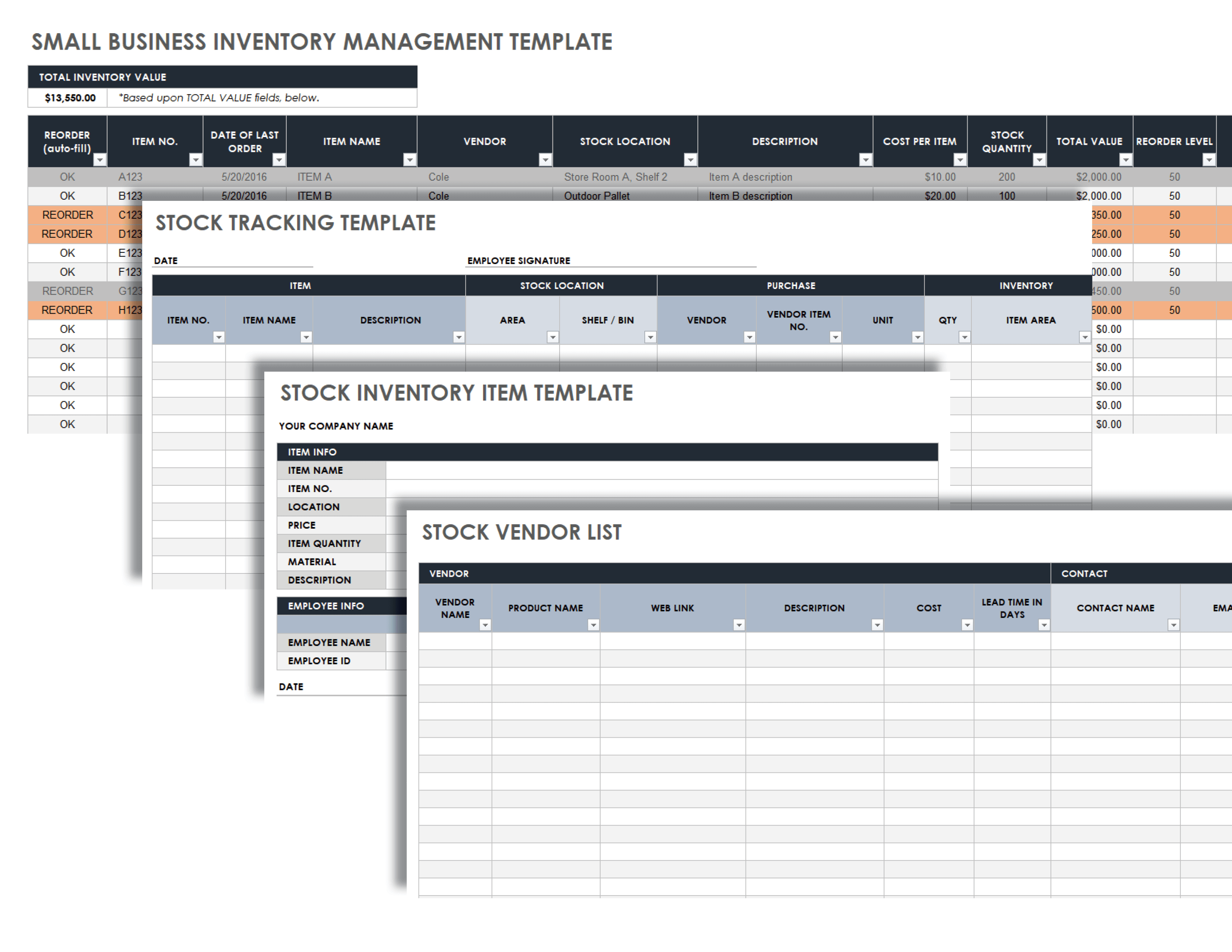
Inventory management for small businesses is a crucial aspect of ensuring operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. By effectively managing inventory levels, small businesses can optimize their cash flow, reduce waste, and enhance their overall profitability.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the fundamentals of inventory management, exploring various methods, tools, and strategies that small businesses can leverage to streamline their operations and achieve inventory optimization.
Understanding Inventory Management for Small Businesses

Inventory management plays a crucial role in the success of any small business. It involves the tracking, organizing, and controlling of the stock items, ensuring that the right products are available at the right time and in the right quantity.
Effective inventory management helps small businesses optimize their cash flow, minimize losses due to overstocking or understocking, and improve customer satisfaction.
Challenges Faced by Small Businesses in Managing Inventory
Small businesses often face unique challenges in managing their inventory. These include:
- Limited resources and storage space
- Difficulty in forecasting demand accurately
- Lack of access to sophisticated inventory management systems
- Competition from larger businesses with more efficient supply chains
Methods for Inventory Management

Inventory management methods help businesses track and control their stock levels to ensure they have the right amount of inventory on hand to meet customer demand. There are several inventory management methods that businesses can use, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
FIFO assumes that the first items purchased are the first items sold. This method is often used for perishable goods, such as food and beverages, to ensure that older items are sold before they expire.
Last-In, First-Out (LIFO)
LIFO assumes that the last items purchased are the first items sold. This method can be advantageous for businesses that expect the cost of goods to increase over time, as it allows them to report lower cost of goods sold and higher profits in the current period.
Additional Inventory Management Methods
- Weighted average cost: This method assigns an average cost to all inventory items, regardless of when they were purchased.
- Specific identification: This method assigns a unique cost to each inventory item, allowing businesses to track the cost of each item sold.
- Just-in-time (JIT): This method aims to minimize inventory levels by ordering only the inventory needed to meet current demand.
- Periodic inventory system: This method involves taking a physical inventory count at regular intervals to determine the value of inventory on hand.
- Perpetual inventory system: This method involves continuously updating inventory records as transactions occur, providing real-time information on inventory levels.
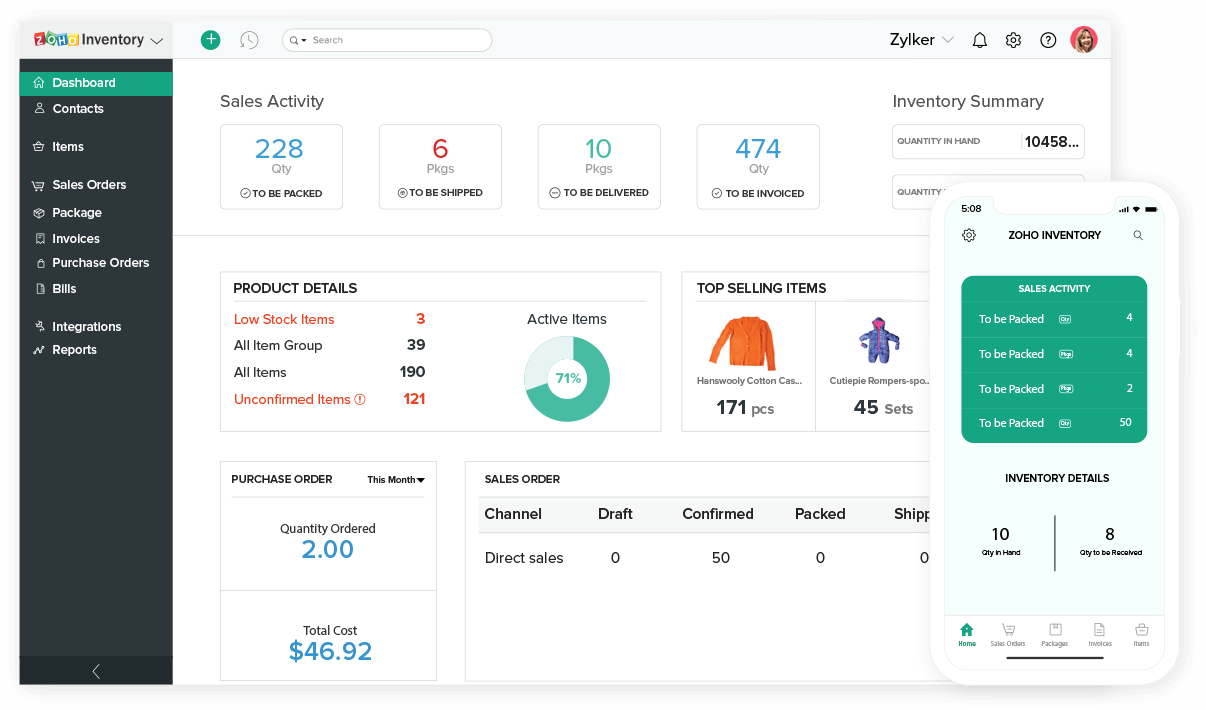
Inventory Management Tools
Inventory management tools streamline inventory tracking and optimize stock levels, offering numerous benefits to small businesses.
These tools provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, enabling businesses to make informed decisions about purchasing, storage, and sales. By automating inventory processes, businesses can reduce manual errors, save time, and improve efficiency.
Types of Inventory Management Tools
- Spreadsheet Software:Basic option for small businesses with limited inventory; requires manual data entry and calculations.
- Dedicated Inventory Management Software:Specialized software designed for inventory tracking, with features like automated updates, inventory forecasting, and reporting.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems:Comprehensive software suites that integrate inventory management with other business functions like accounting and customer relationship management.
Selecting the Right Tool
Consider the following factors when selecting an inventory management tool:
- Inventory Volume:Choose a tool that can handle the volume of inventory you manage.
- Business Needs:Determine the specific features and functionality you require, such as inventory forecasting or multi-location support.
- Budget:Set a budget and compare the cost of different tools.
- Integration:Consider how the tool will integrate with your existing systems, such as accounting software or e-commerce platforms.
- User-Friendliness:Ensure the tool is easy to use and navigate for your team.
Optimizing Inventory Levels
Maintaining optimal inventory levels is crucial for small businesses to balance customer satisfaction, minimize costs, and ensure efficient operations.
Determining the ideal inventory level involves a delicate balancing act. Overstocking can lead to excess storage costs, product obsolescence, and cash flow issues, while understocking can result in lost sales, customer dissatisfaction, and missed revenue opportunities.
Strategies for Determining Optimal Inventory Levels
- ABC Analysis:Classify inventory items based on their value and usage patterns (high-value, medium-value, low-value). Focus on managing high-value items more closely to minimize risk.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ):Calculate the optimal quantity to order at a time, considering factors such as demand, holding costs, and ordering costs.
- Safety Stock:Maintain a buffer inventory to cushion against unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply chain disruptions.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory:Minimize inventory by ordering only what is needed, when it is needed, reducing storage costs and obsolescence.
Consequences of Overstocking
- Increased storage and insurance costs
- Product deterioration and obsolescence
- Tied-up cash flow
- Inefficient use of warehouse space
Consequences of Understocking
- Lost sales and customer dissatisfaction
- Increased order frequency and shipping costs
- Potential for production delays
- Damage to reputation
Inventory Tracking and Control
Inventory tracking and control are crucial aspects of inventory management for small businesses. Effective tracking enables businesses to monitor inventory levels, identify discrepancies, and prevent stockouts or overstocking. Inventory control involves implementing measures to safeguard inventory from theft, damage, or loss.
Inventory Tracking Methods
- Manual Tracking:Using pen and paper or spreadsheets to record inventory levels and transactions.
- Barcode Scanning:Assigning unique barcodes to products and using barcode scanners to track their movement.
- RFID (Radio Frequency Identification):Utilizing RFID tags attached to products to track their location and movement using RFID readers.
- Inventory Management Software:Specialized software that automates inventory tracking and provides real-time visibility into inventory levels.
Importance of Inventory Control
Inventory control is essential to protect inventory assets and prevent losses. It involves:
- Physical Security:Implementing measures such as security cameras, access control systems, and secure storage facilities to prevent theft.
- Environmental Control:Ensuring proper storage conditions, such as temperature and humidity control, to prevent damage to inventory.
- Inventory Audits:Regularly conducting physical counts of inventory to verify accuracy and identify discrepancies.
- Cycle Counting:Periodically counting a portion of inventory to identify and correct errors before they become significant.
Benefits of Effective Inventory Management
Effective inventory management practices offer numerous benefits that positively impact a small business’s financial performance, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
Financial Benefits
Accurate inventory management allows businesses to optimize stock levels, reducing the risk of overstocking and subsequent losses due to unsold inventory. Additionally, it helps minimize the cost of holding inventory, including storage, insurance, and handling expenses. Efficient inventory management also enables businesses to identify and eliminate obsolete or slow-moving items, freeing up capital for more profitable investments.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Effective inventory management ensures that businesses can meet customer demand consistently. By maintaining optimal stock levels, businesses can fulfill orders promptly, reducing the likelihood of backorders and customer dissatisfaction. Additionally, accurate inventory information allows businesses to provide reliable delivery estimates, enhancing customer confidence and loyalty.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Optimized inventory levels streamline business operations by reducing the time and resources spent on inventory-related tasks. Efficient inventory management systems automate inventory tracking and replenishment processes, freeing up staff for more value-added activities. Additionally, it helps prevent stockouts, ensuring smooth production and delivery schedules, and reducing the need for expedited shipping or emergency orders.
Case Studies and Best Practices
Small businesses can learn from the successes and challenges of others. Here are some case studies of successful inventory management practices by small businesses:
- Company A:A small online retailer implemented a cloud-based inventory management system. This system automated inventory tracking, reduced errors, and improved customer satisfaction.
- Company B:A small manufacturing company used a just-in-time inventory system to reduce waste and improve cash flow.
- Company C:A small retail store used a perpetual inventory system to keep track of inventory levels in real-time. This system helped the store avoid stockouts and overstocking.
These case studies highlight the benefits of effective inventory management for small businesses. By implementing best practices, small businesses can improve their efficiency, profitability, and customer satisfaction.
Best Practices for Inventory Management in Small Businesses
Here are some best practices for inventory management in small businesses:
- Use a centralized inventory management system:This will help you track inventory levels across all locations and channels.
- Implement a just-in-time inventory system:This will help you reduce waste and improve cash flow.
- Use a perpetual inventory system:This will help you keep track of inventory levels in real-time.
- Set safety stock levels:This will help you avoid stockouts.
- Monitor inventory levels regularly:This will help you identify trends and make adjustments as needed.
- Use inventory management software:This can help you automate inventory tracking and improve efficiency.
By implementing these best practices, small businesses can improve their inventory management and achieve a number of benefits.
Recommendations for Implementing Best Practices, Inventory management for small business
Here are some recommendations for implementing best practices for inventory management in small businesses:
- Start by assessing your current inventory management practices.Identify areas where you can improve.
- Choose an inventory management system that meets your needs.There are many different systems available, so it’s important to find one that is right for your business.
- Implement the system gradually.Don’t try to change everything at once. Start with a few key changes and then add more as you become more comfortable with the system.
- Train your staff on the new system.Make sure they understand how to use the system and how it will benefit the business.
- Monitor your inventory levels regularly.This will help you identify trends and make adjustments as needed.
By following these recommendations, small businesses can successfully implement best practices for inventory management and achieve a number of benefits.
Wrap-Up

Effective inventory management is a cornerstone of success for small businesses. By implementing the principles and strategies Artikeld in this guide, small businesses can gain a competitive edge, enhance their financial performance, and position themselves for long-term growth.
FAQ Explained
What is the significance of inventory management for small businesses?
Inventory management is essential for small businesses to optimize cash flow, reduce waste, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance operational efficiency.
What are the common challenges faced by small businesses in managing inventory?
Small businesses often face challenges such as limited storage space, fluctuating demand, and difficulties in forecasting inventory needs.
What is the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method of inventory management?
FIFO is an inventory management method that assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first, ensuring that perishable goods are sold before they expire.